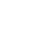
Figure 1 Distribution of evapotranspiration and surface temperature in urban areas (Peking University Shenzhen Campus)
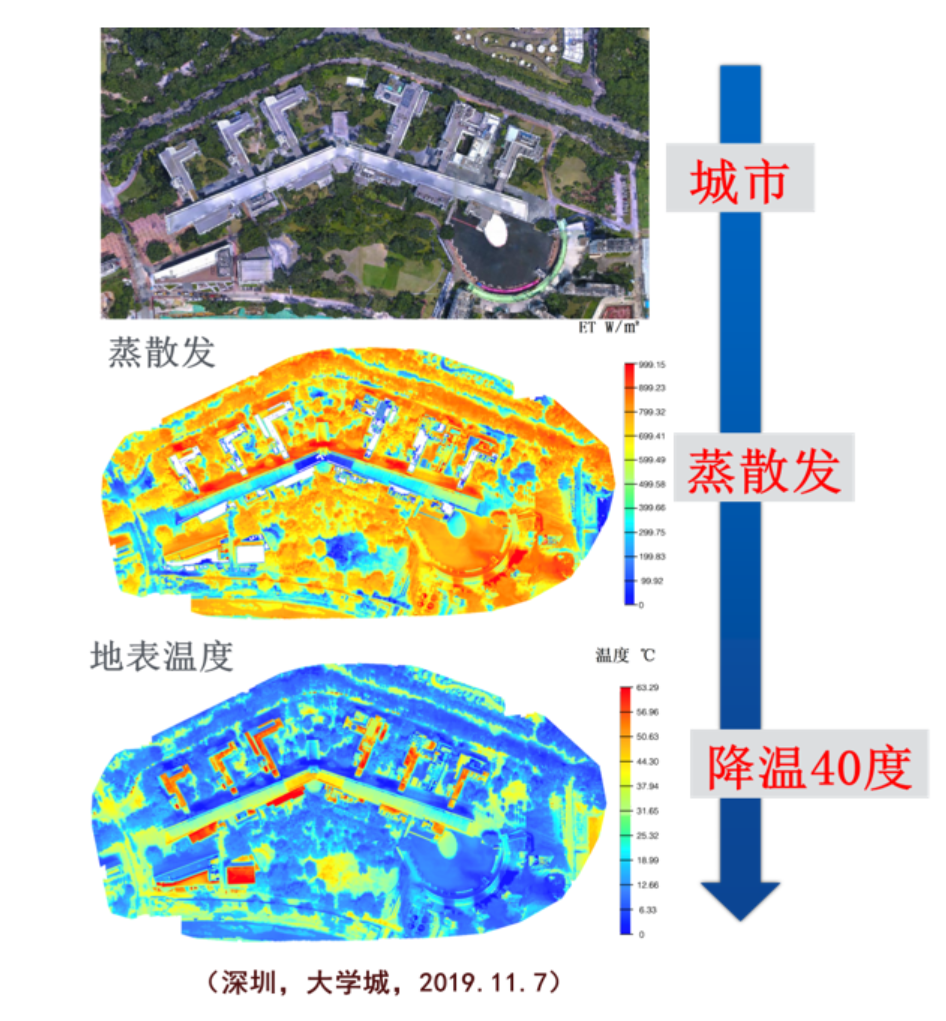
Fig. 2 Spatial and temporal variation of evapotranspiration in urban areas (Peking University Shenzhen Campus)
2. Development of Air Purification Technology for Internal Combustion Engines
The Warp Air Clean product, developed in collaboration with our laboratory is compact, requires no changes to vehicle or engine structures, and can be easily installed in front of the vehicle’s air filter. This technology can reduce HC and CO emissions by 80%, black smoke emissions by 20-80%, diesel fuel consumption by 6-10%, and gasoline fuel consumption by 10%. With a lifespan of 2 years, the product’s fuel savings can recover the cost within 6 months, providing significant environmental and economic benefits.

Figure 3 Warp Air Clean products, left for cars, right for trucks
3. Development and Application of a Flying Intelligent Environmental Monitoring Robot
The flying intelligent environmental monitoring robot, developed by the laboratory after over 10 years of research, integrates theoretical algorithms, multi-source sensors, big data, and unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs), and has already obtained 11 intellectual property rights. Unlike drones that only take photos, this product is a new generation flying robot with eyes, a brain, and a soul, driven by our innovative theoretical algorithms. The product is expected to significantly replace human labor in many industries and fields, becoming a norm in society and workplaces.
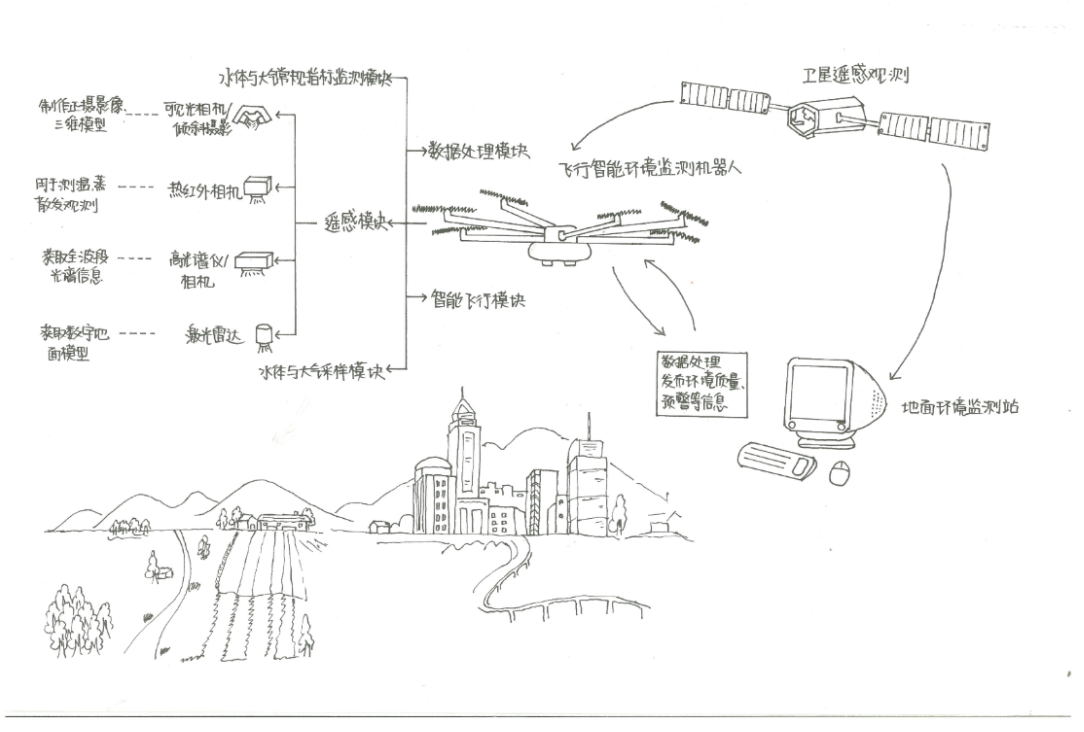
Figure 4: Schematic of the Flying Intelligent Environmental Monitoring Robot Product
This robot has the ability to execute multiple types of projects, integrate various UAV platforms, utilize various data acquisition devices (optical, spectral, infrared, lidar), and perform multi-source data coupling and big data analysis, among other capabilities.
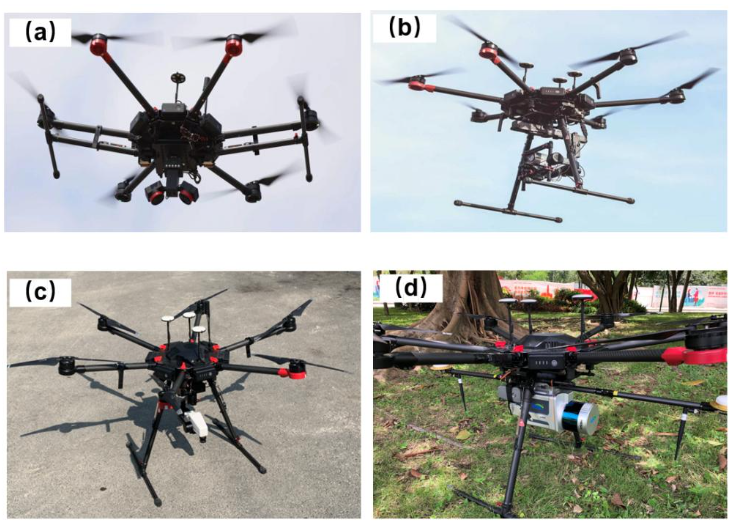

Figure 5: Integration of Different Onboard Sensors:(a) Dual-lens Tilted Photography System;(b) Multispectral and Thermal Infrared Camera System;(c) Hyperspectral System;(d) Lidar System
Currently, the laboratory is conducting various applications and studies using the flying intelligent environmental monitoring robot, including post-earthquake landslide assessments, vegetation loss monitoring after typhoons, urban water quality evaluations, and monitoring urban heat islands and heatwaves.

Figure 6: Post-earthquake Recovery Quantitative Assessment Based on UAV Remote Sensing
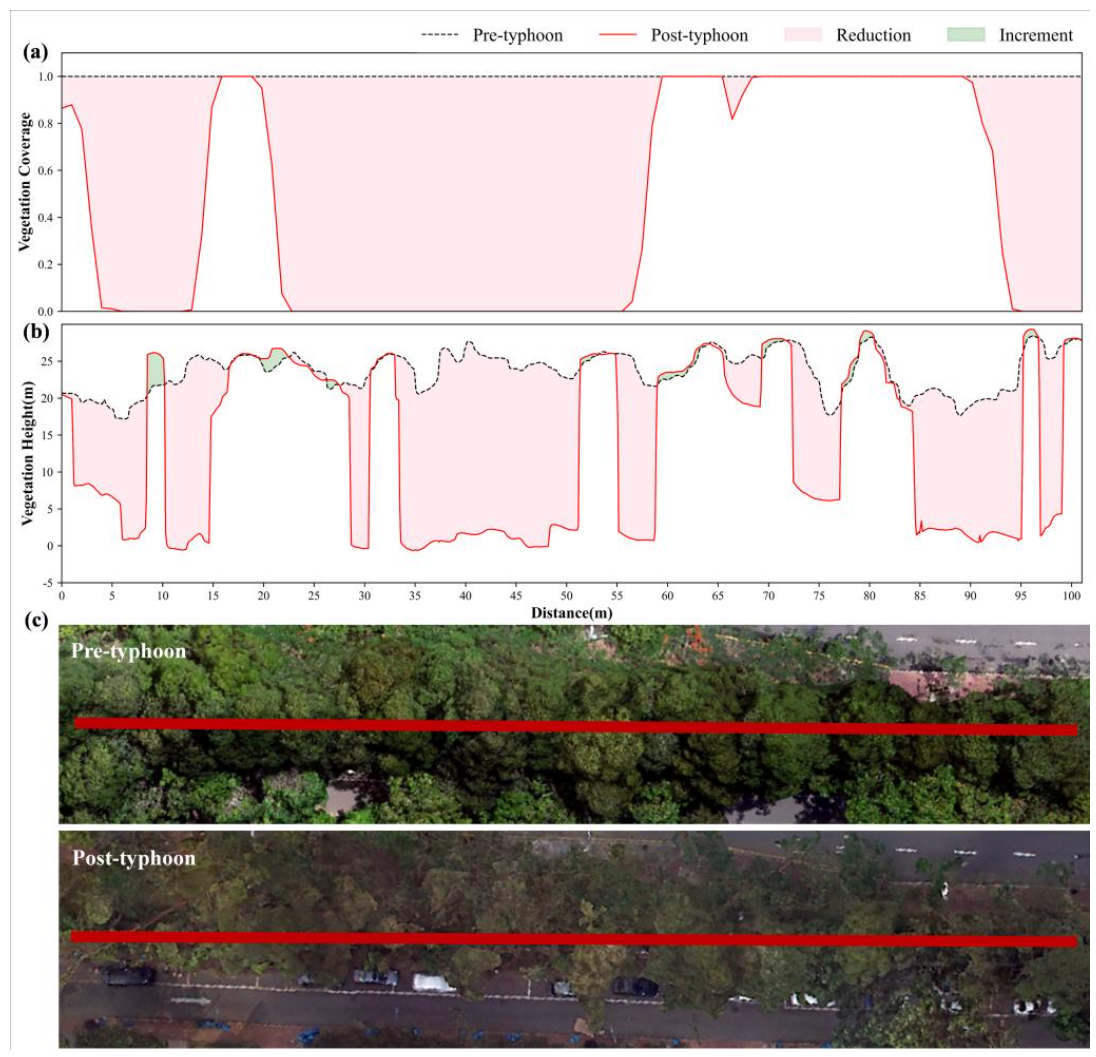
Figure 8: Post-typhoon Loss Assessment from “Mangkhut” Based on UAV Remote Sensing.
Changes in canopy coverage and height of street trees before and after the typhoon:(a) Vegetation Coverage; (b) Vegetation Height; (c) Sample Line Position
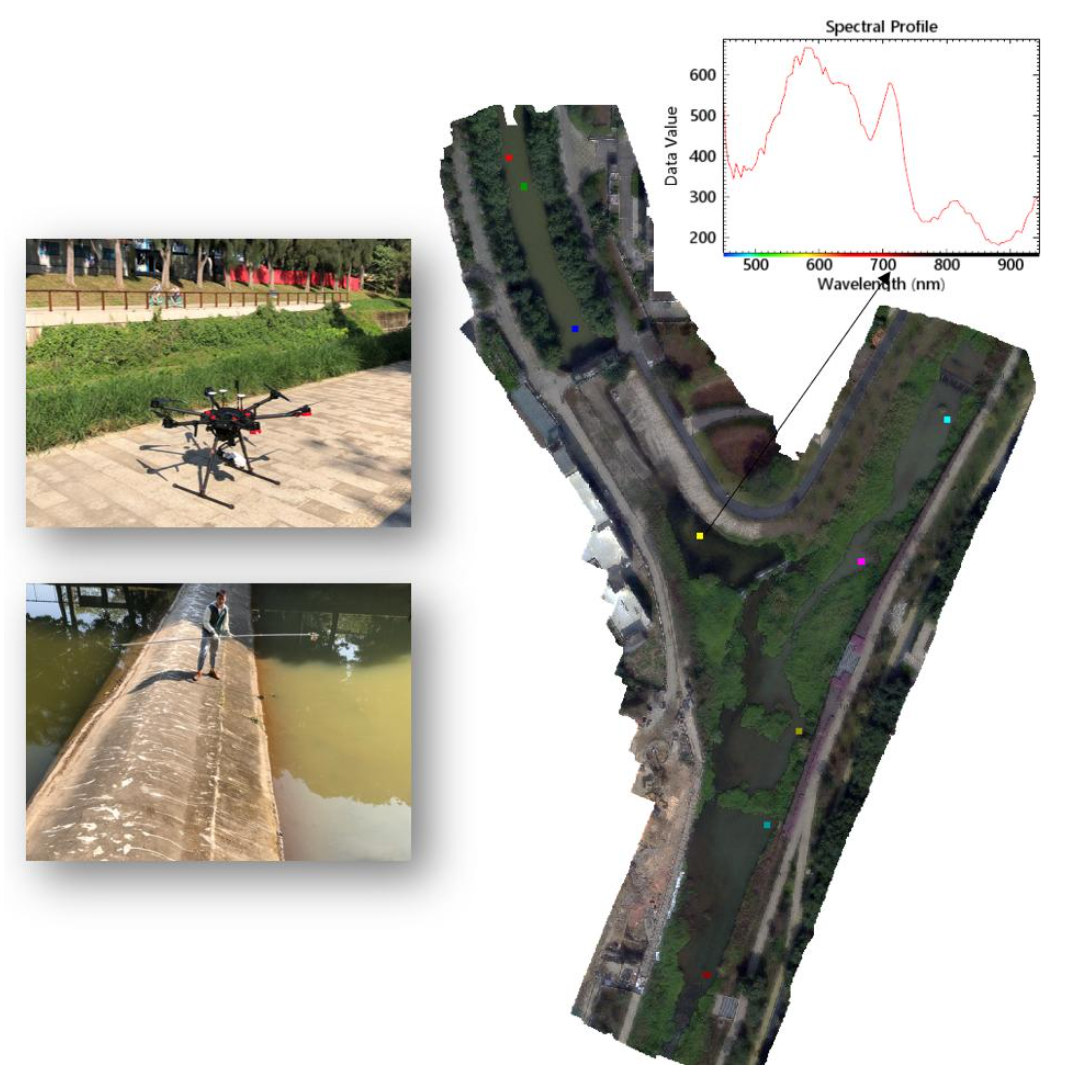

Figure 9: Urban Water Quality Assessment Based on UAV Remote Sensing
Laboratory Instruments and Equipment Introduction
The laboratory boasts world-leading equipment and instruments in the environmental and energy research field, especially in the study of evapotranspiration. It is regarded as the laboratory with the best instrumentation in this area.
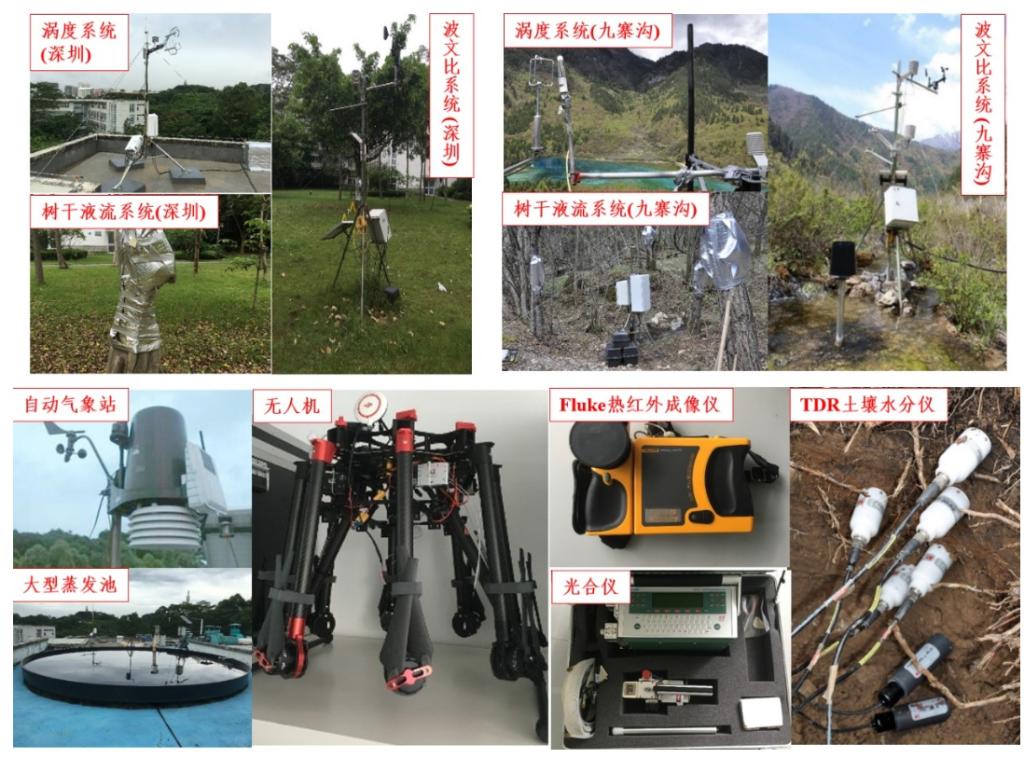
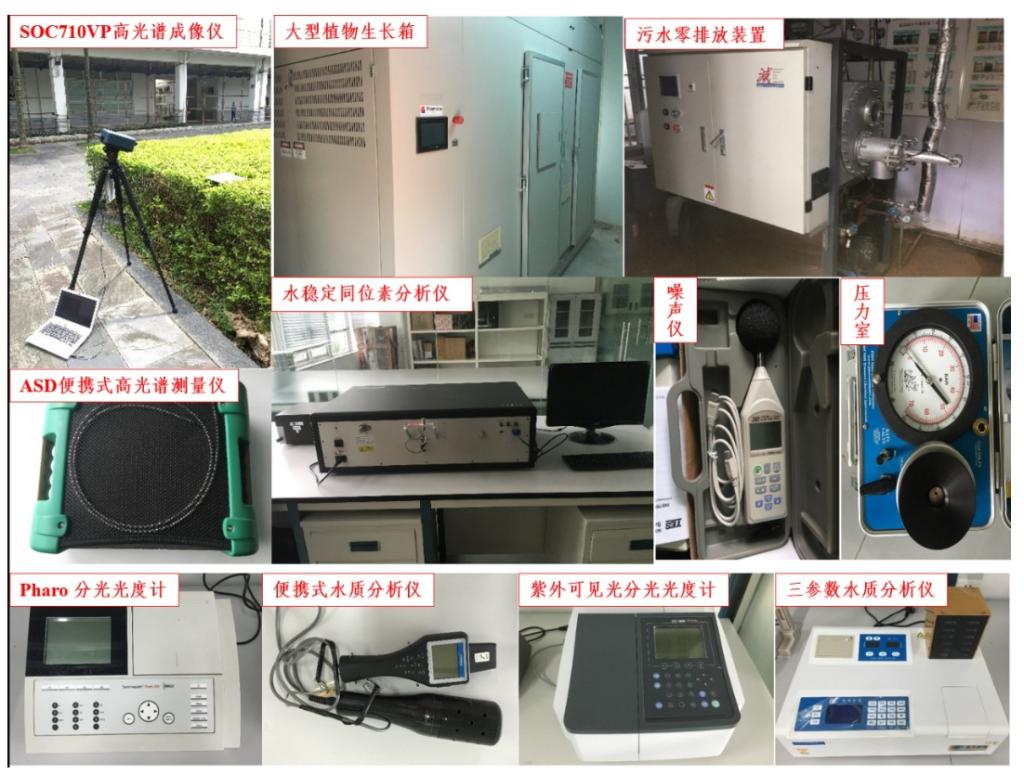
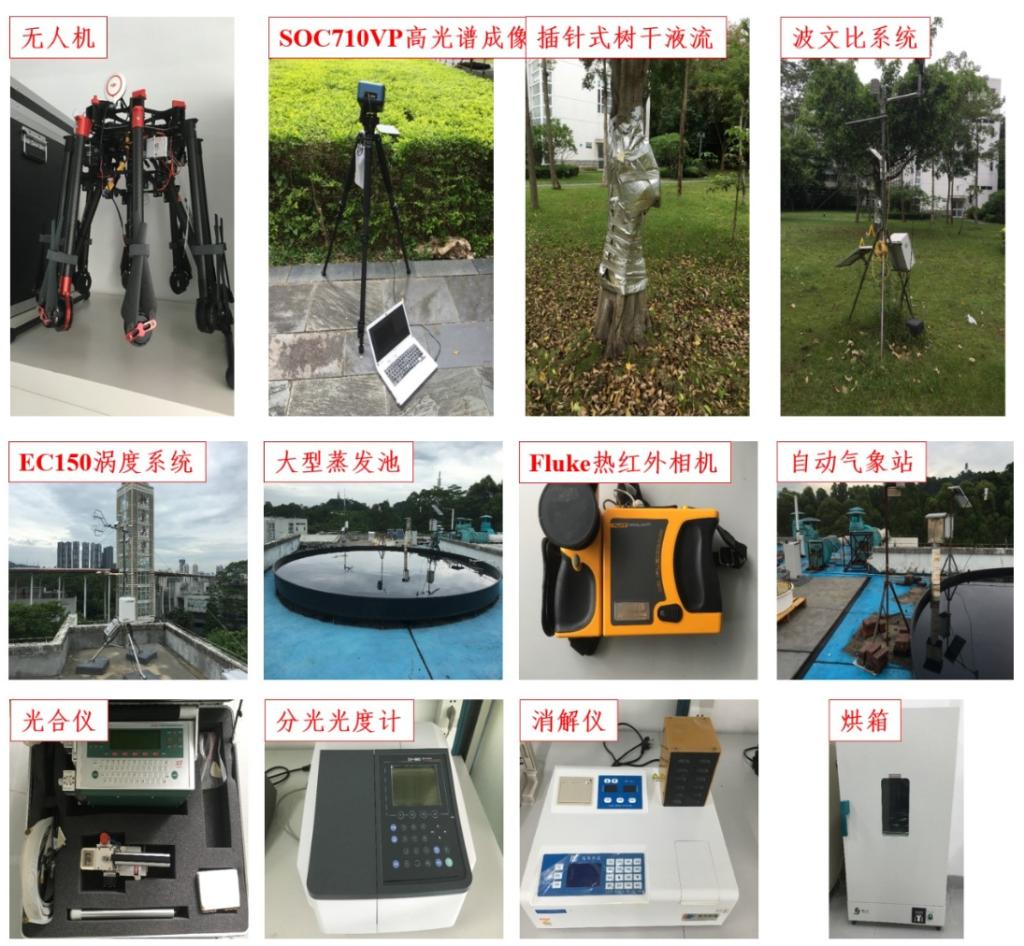





Figure 10: Laboratory Instruments and Equipment Overview
We welcome outstanding students with a background in science and engineering to join our team:

Here, there are the footprints of you pursuing your dreams, and the youth of you working hard for your ideals, paying for your ideals, struggling for your ideals and harvesting for your ideals! Come, excellent students, we are waiting for you eagerly with open arms.